-
Continuous reaction technology solutions
 High-risk process product solutions
High-risk process product solutions Continuous post-processing technology solutions
Continuous post-processing technology solutions Continuous pharmaceutical formulation solutions
Continuous pharmaceutical formulation solutions Safety analysis of fine chemicals, first-time process reliability evaluation solutions
Safety analysis of fine chemicals, first-time process reliability evaluation solutions Continuous flow multi-function platform solutions
Continuous flow multi-function platform solutions Reaction type solutions
Reaction type solutions
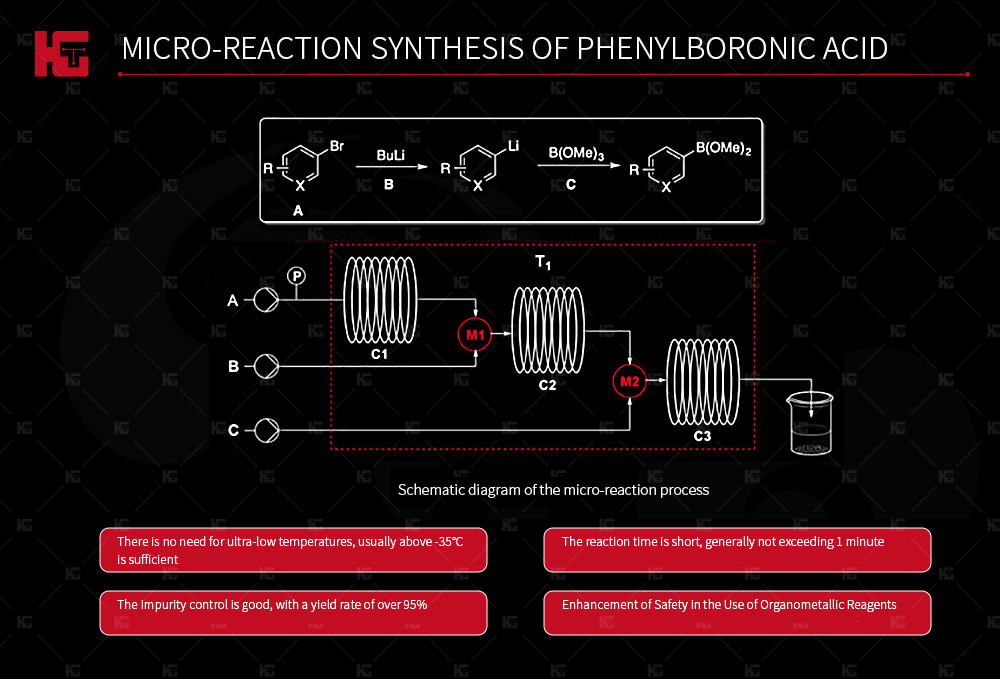
Drug synthesis often uses organic metal reagents such as butyllithium and LDA. These reaction reagents are highly dangerous and prone to ignition. The reagents themselves are easily hydrolyzed and require high reaction system and operation skills, which can lead to difficulties in repeatability of the reaction.
Metal-organic reactions typically require the use of methods such as liquid nitrogen to control extremely low temperatures (e.g., -78℃). However, this is not the temperature required by the reaction itself, but rather due to the heat transfer limitations of the reaction equipment. In order to reduce reaction hotspots, a lower reaction temperature is used. In microreactors, such reactions can often achieve good results at around -35℃, and the selectivity is often significantly improved.
Prev: chlorination reaction
Next: Peroxide reaction